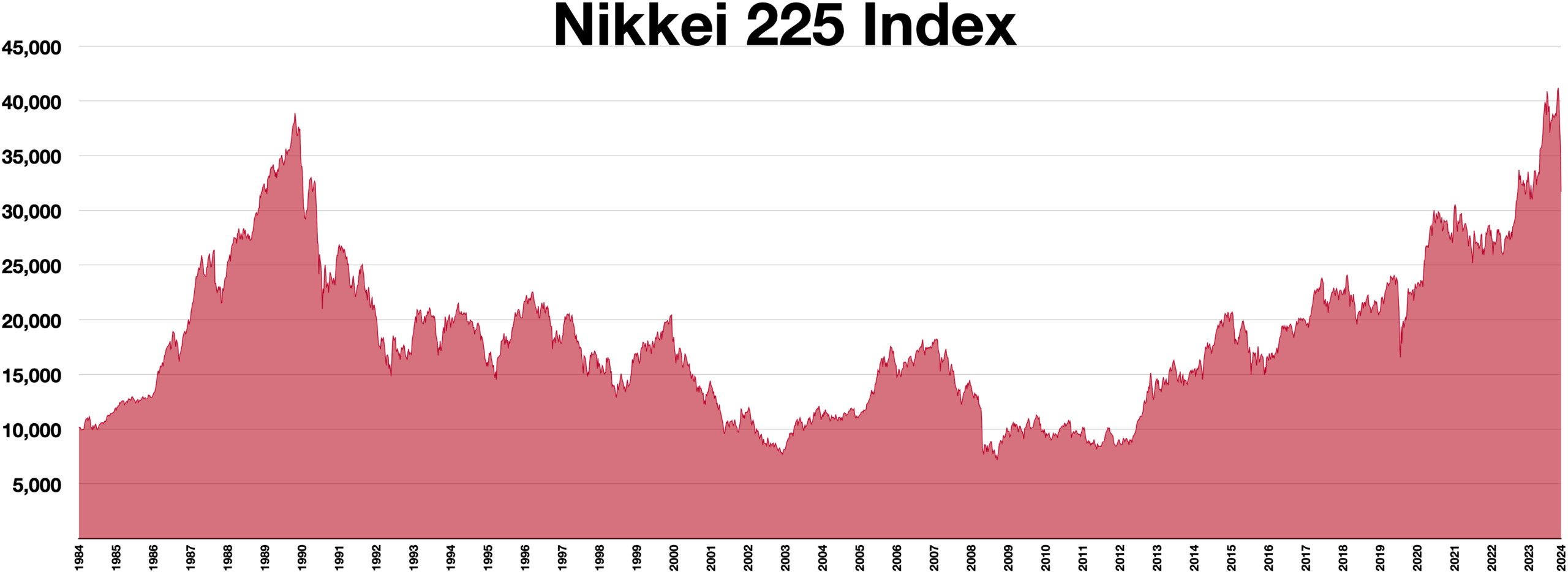
What is the Nikkei Index?
The Nikkei Index, officially known as the Nikkei 225, is a stock market index that tracks the performance of the top 225 blue-chip companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE). Serving as a critical barometer for understanding Japan’s economic health, the index is widely regarded by investors and analysts alike as a significant indicator of the nation’s financial market trends. Established in 1950, the Nikkei Index marked its inception in a post-war Japan, providing essential insights into the recovery and growth of the country’s economy during a time of significant change.
The historical significance of the Nikkei Index cannot be overstated. It symbolizes not only the performance of specific companies but also reflects broader economic trends, domestic policies, and global market dynamics affecting Japan. The index is calculated using a price-weighted methodology, meaning that companies with higher stock prices have a greater impact on the index’s overall movement. Some of the most notable companies included in the Nikkei 225 range from giants in technology and automotive industries to major financial institutions.
Factors Influencing the Nikkei Index
The Nikkei Index, representing Japan’s stock market, is subject to a multitude of influencing factors. Among the most significant are various economic indicators, including Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, unemployment rates, and inflation levels. A growing GDP typically suggests a healthy and expanding economy, which tends to boost investor confidence and drive stock prices higher, consequently uplifting the Nikkei Index. Conversely, when GDP growth stagnates or declines, it can lead to decreased investor sentiment and a subsequent drop in stock values.
Unemployment rates serve as another critical gauge, as high unemployment often correlates with economic distress, affecting consumption patterns and overall economic health. A significant rise in unemployment may indicate vulnerabilities within the economy, potentially leading to lowered stock prices and a dip in the Nikkei Index. Additionally, inflation is an essential factor; moderate inflation might indicate a thriving economy, but excessive inflation could erode purchasing power and trigger central bank intervention, impacting the stock market adversely.
Global market trends also play a pivotal role in shaping the fluctuations of the Nikkei Index. Economic interdependence means that developments in other major economies can have a ripple effect on Japan. For instance, if the United States or China experiences economic upheaval, it can lead to concerns about export demand and overall economic stability in Japan, affecting the Nikkei. Political stability is another fundamental component; stable governance fosters investor confidence and mitigates uncertainty, while political unrest can induce volatility.
Furthermore, major events, including natural disasters and significant policy changes, can greatly impact market sentiment. Japan’s susceptibility to earthquakes and other disasters can result in immediate but sometimes short-lived impacts on the Nikkei Index. Hence, understanding these multitude of factors provides insights into the dynamic nature of the Nikkei Index and its reflection of Japan’s economic landscape.
Investment Opportunities and Strategies in the Nikkei Index
The Nikkei Index, a vital barometer for Japan’s economic performance, presents various investment opportunities for both novice and experienced investors. One of the most accessible ways to gain exposure to the Nikkei is through exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These financial products allow investors to buy shares that track the performance of the Nikkei 225, providing an efficient means to diversify portfolio holdings without the need for extensive research into individual stocks. Several ETFs are available that focus exclusively on the Nikkei, enabling investors to capitalize on its performance while minimizing risks associated with single-stock investments.
Another avenue for investment is mutual funds that focus on Japanese equities, particularly those that concentrate on stocks within the Nikkei Index. These funds are typically managed by professionals who use their expertise to select and manage a diversified portfolio, which can benefit investors who prefer a hands-off approach. By investing in these mutual funds, individuals can harness the potential growth associated with Japan’s economic landscape while relying on the expertise of fund managers. Furthermore, direct stock investments in the constituent companies of the Nikkei Index can also be a lucrative option. This strategy requires an in-depth understanding of the companies and sectors represented in the index, making it more suitable for seasoned investors who can conduct thorough analyses.
When formulating investment strategies specific to the Nikkei Index, investors may consider various methodologies such as value investing, which involves identifying undervalued stocks within the index, or growth investing, which focuses on companies with strong potential for future expansion. Moreover, implementing effective risk management techniques tailored to the Japanese markets can safeguard investments during economic fluctuations. These may include setting stop-loss orders, diversifying investments across various sectors, and regularly reviewing portfolios in response to market trends. By applying these strategies, investors can better navigate the complexities of the Nikkei Index and enhance their prospects for financial success.
The Future Outlook of the Nikkei Index
The future outlook of the Nikkei Index is subject to a variety of influential factors that could shape its trajectory in the coming years. Currently, many experts point to technological advancements as a significant driver of the index’s performance. The acceleration of innovation in sectors like artificial intelligence, robotics, and green technologies places Japan at the forefront of major transformations. Companies listed on the Nikkei will likely benefit from increased investment in these areas, potentially resulting in strong growth and better index performance.
Another prominent aspect influencing the Nikkei Index is demographic shifts. Japan’s population is aging, leading to a shrinking workforce but also heightening demand for healthcare services and technologies. This situation creates a dual pathway: on one hand, it may challenge traditional sectors; on the other, it opens new avenues for growth in industries that cater to the elderly population. As such, firms that align their business models with these demographic trends may contribute positively to the overall index.
Potential regulatory changes and economic policies also pose a significant impact on the future of the Nikkei Index. The Japanese government has been focusing on reforms aimed at stimulating economic growth, including deregulation and financial incentives for investors. Such policies could enhance market sentiment and encourage foreign investments, contributing positively to the index’s performance. Additionally, experts suggest keeping an eye on global economic conditions, particularly the influence of major economies like the United States and China, which can ripple through global markets, affecting the Nikkei as well.
Overall, while the future of the Nikkei Index remains uncertain, through analyzing technological progress, demographic changes, and regulatory developments, a clearer picture can be painted. Market forecasts are hopeful, with many analysts suggesting that the index could reach new highs as Japanese industries adapt to these evolving trends.